Difference between revisions of "Map"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 49: | Line 49: | ||
[[File:Legend.png]] | [[File:Legend.png]] | ||
<li>Add Layers to the Map in the section titled “Layers” by selecting from the drop down menu and clicking the left-hand facing arrow or create a new “Layer” record by clicking the star button (See “Creating a Layer” section for instructions)</li> | <li>Add Layers to the Map in the section titled “Layers” by selecting from the drop down menu and clicking the left-hand facing arrow or create a new “Layer” record by clicking the star button (See “Creating a Layer” section for instructions)</li> | ||
| + | [[File:Layer.png]] | ||
| + | <li>Click “Create”</li> | ||
| + | <li>To add a data series to the Map, you will need to add an influence to the Map (See “Creating an Influence” section for instructions)</li> | ||
| + | |||
<ol type="i"> | <ol type="i"> | ||
Revision as of 12:40, 16 July 2014
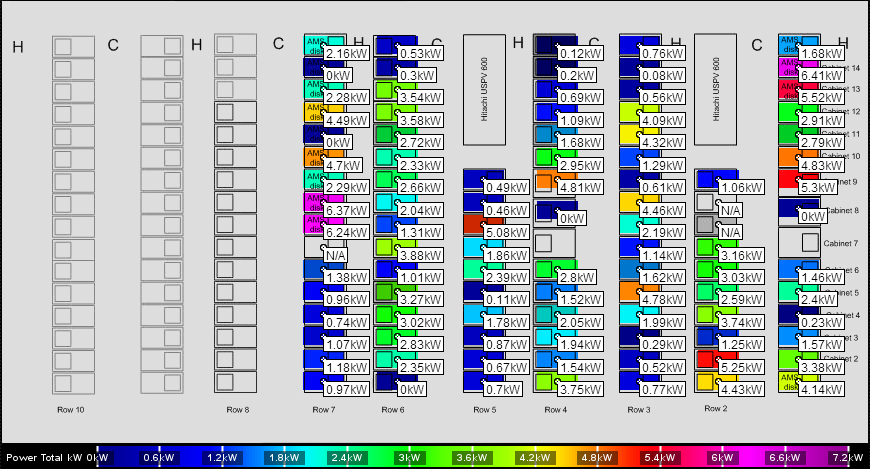
A Map is a customizable representation of data where individual values contained in the visual are shown by colors. Fed by Data Series, a Map can show many different types of data, such as power usage, temperature, humidity, etc. A Map does not just need to be an image of your data center, you can place an influence on any transparent image uploaded into LiveDC.
You will need to gather the following information prior to creating a Map:
- Name of the Map
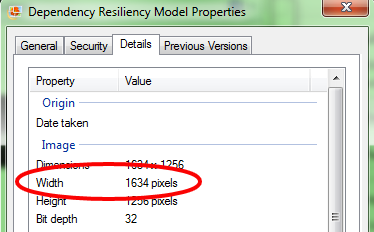
- Width in Pixels of the Map (determined by looking at the properties of the image)
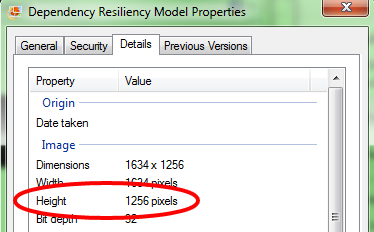
- Height in Pixels of the Map (determined by looking at the properties of the image)
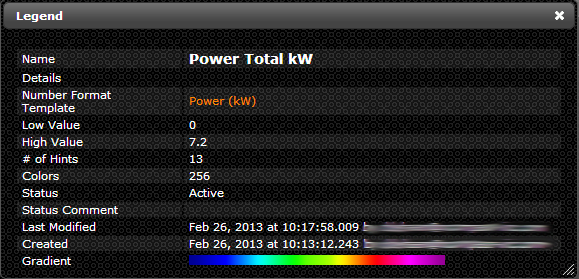
- The Legend that corresponds with the Map (Temp, Humidity, Power, Cost, etc.)
- This is the representative color scale you see at the bottom of each Map
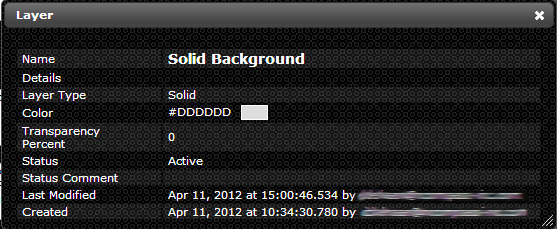
- The Layers that will make up your Map (Solid Background, Influences Layer, Transparent Floor Layout, etc.)
- Most Maps are made of those three (3) Layers
- A good way to make your floor layout transparent is to use an open source program called GIMP, which can be downloaded from the web.
- Import the floor layout into GIMP
- Change all colors to “Gray scale” by selecting mode under the image menu
- Create a Black Border for the floor layout using the selection tool under the Tools menu in GIMP
- Select ‘Color to Alpha’ from the colors menu to change the selected area into a transparent part fo the image
- Export the image as a .PNG file and save to your preferred location
- Import the PNG file into LiveDC utilizing the “Uploaded Images” feature (See “Uploading an Image” for more information)
Contents
Creating a Map
- On the navigation menu (left-hand side) click “Visuals” and click “Maps” this will open a new tab titled “Maps”
- Within the Maps tab, in the upper left-hand corner click the “Create” button. A new window will open up called “Create Map”
- Enter the name of the Map in the “Name” field
- Examples: Operational Model – Cooling, Power %, Operational Cost per Cabinet, etc.
- Enter any additional information about the Map in the “Details” field
- Define a horizontal size in pixels for the Map in the “Width” field
- A good rule of thumb is to look at the Properties of the Image and use those predefined dimensions (usually no more than 1650 pixels)
- If you have an image larger than that, you can scale the image down to a smaller size before importing)
- Define a vertical size in pixels for the Map in the “Height” field
- A good rule of thumb is to look at the Properties of the Image and use those predefined dimensions (usually no more than 1300 pixels)
- If you have an image larger than that, you can scale the image down to a smaller size before importing))
- Add a Legend to the Map in the section titled “Legends” by selecting from the drop down menu and clicking the left-hand facing arrow or create a new “Legend” record by clicking the star button (See “Creating a Legend” section for instructions)
- Add Layers to the Map in the section titled “Layers” by selecting from the drop down menu and clicking the left-hand facing arrow or create a new “Layer” record by clicking the star button (See “Creating a Layer” section for instructions)
- Click “Create”
- To add a data series to the Map, you will need to add an influence to the Map (See “Creating an Influence” section for instructions)
- If you select “Dynamic Set” you will need to fill in additional information. A dynamic set allows you perform a function on a set of data which is categorized by tags, for example Average Cold Aisle temperature would take all data series with the tag "cold aisle" and average them out to give you one data point. The additional information needed is:
- Data points start date
- Inclusion - All, Any
- Tags: Select from the drop down menu and click the left-hand facing arrow or create a new “Tag” record by clicking the star button (See “Creating a Tag” section for instructions)
- Operation - Average, Maximum, Median, Minimum, Sum
- Adjustment Expression
- If you select “Formula” you will need to fill in additional information. A formula data series allows you to apply logic to a number of data series, for example Difference of Power in Cabinet 1 and Cabinet 2 would take these two data series and subtract them from each other to give you one data point. The additional information needed is:
- Data points start date
- Formula- what you want to do with the data points outlined in number 3 below, example syntax: v0 - v1, where v0 = Power in cabinet 1 and v1 = Power in cabinet or additional variables can be used in the formula and would be referenced as v3, v4, etc.
- Values: Select from the drop down menu and click the left-hand facing arrow or create a new “Value” record by clicking the star button (See Creating a Data Series section for instructions)
- Adjustment Expression
- If you select “Record Count” you will need to fill in additional information. A record count data series allows you to get a count of how many data series contain a specific tag or set of tags. The record count data series leverages the search capability built in to LiveDC. The additional information needed is:
- Data points start date
- Search Criteria: Select from the drop down menu or create a new “Search Criteria” record by clicking the star button (See “Creating a Saved Search Criteria” section for instructions)
- Adjustment Expression
- If you select “SNMPv1” you will need to fill in additional information. An SNMPv1 data series polls intelligent devices that talk SNMP and you specify the interval at which you want to request this data. The additional information needed is:
- Collector Assignment - usually use Automatic
- SNMPV1 Template: Select from the drop down menu or create a new “SNMPv1 Template” by clicking the star button (See “Creating a SNMPv1 Template” section for instructions)
- Address - IP Address
- Read Community String - usually by default this is "Public"
- Regular Expression - usually left blank
- SNMP OID
- If you select “Trend” you will need to fill in additional information. A trend data series allows you to look at a standard data series over a period of time, for example if you had the power of a cabinet over the last year you could set up a trend data series to use the power data series and look at a trend over the last 3 months. The additional information needed is:
- Data points start date
- Data series to trend. Select from the drop down menu or create a new “Data Series to Trend” record by clicking the star button (See Creating a Data Series section for instructions)
- Trend template: Select from the drop down menu or create a new “Trend Template” record by clicking the star button (See “Creating a Trend Template” section for instructions)
- Adjustment Expression
- If you select “URL Scrape” you will need to fill in additional information. A URL Scrape data series allows you to pull information from an unsecured web page using regex to determine the location of the information on the webpage.
- Collector Assignment - usually use Automatic
- URL Scrape Template: Select from the drop down menu or create a new “URL Scrape Template” record by clicking the star button (See “Creating a URL Scrape Template” section for instructions)
- Regular Expression
- URL - website to find the information
- Click "Create"
- You now have a data series that will be collecting data on the interval you specified and the data series will be able to be used in Maps, Graphs and LiveTiles.